Molecule Profile
-
Chemical Name: Mitochondrial Open Reading Frame of the 12S rRNA-c
-
Sequence: Met-Arg-Trp-Gln-Glu-Met-Gly-Tyr-Ile-Phe-Tyr-Pro-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg
-
Molecular Formula: C₁₀₁H₁₅₂N₂₈O₂₂S₂
-
Molecular Weight: 2174.62 g/mol
-
PubChem CID: 146675088
-
Solubility: Soluble in water; reconstitution in sterile or bacteriostatic water is required.
Product Overview
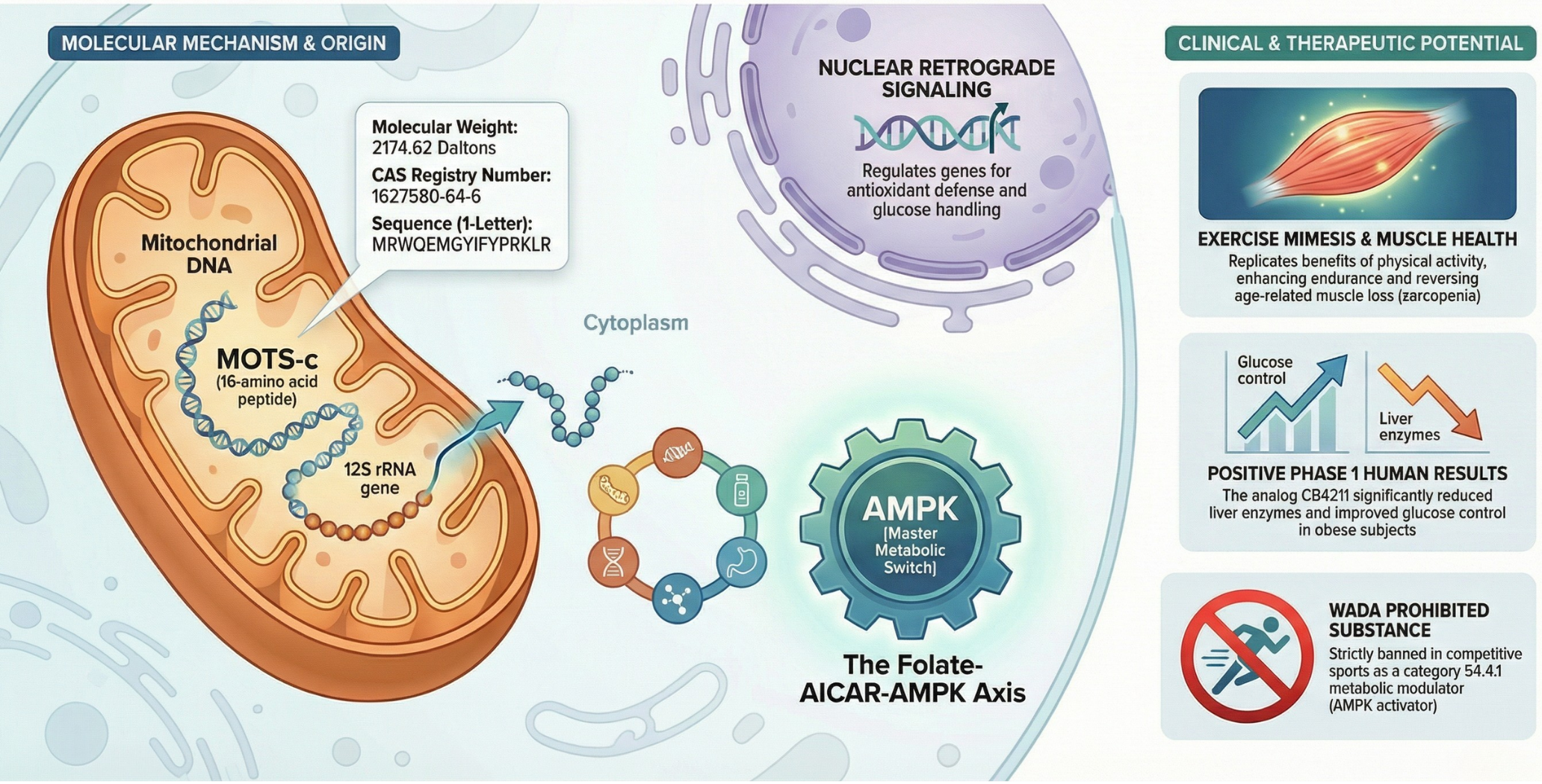
MOTS-c is a pioneering mitochondrial-derived peptide (MDP) involved in systemic metabolic communication and retrograde signaling between the mitochondrial network and the nuclear genome. It functions by inhibiting the folate cycle to facilitate the accumulation of AICAR, which subsequently triggers the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)—the cell’s master metabolic switch. This activation promotes catabolic pathways such as glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation while inhibiting anabolic processes in experimental models. Beyond its role in energy homeostasis, MOTS-c serves as a stress-responsive signaling molecule that translocates to the nucleus to interact with transcription factors like NRF2, influencing cellular resilience. Preclinical research utilizes MOTS-c to investigate metabolic flexibility, exercise mimesis, age-related functional decline, and tissue-specific lipid regulation.
Key Areas of Research
Note: The following observations are derived exclusively from in-vitro and in-vivo animal models.
1. Metabolic Flexibility and Glucose Homeostasis In research models of diet-induced obesity, MOTS-c has been observed to prevent insulin resistance by upregulating GLUT4 translocation in skeletal muscle, allowing for insulin-independent glucose disposal. It participates in “metabolic rewiring” by promoting the “browning” of white adipose tissue, which increases energy expenditure through thermogenesis even in sedentary states.
2. Geroprotection and Muscle Preservation Studies investigate MOTS-c as a regulator of physical longevity. In aged animal models, the peptide has demonstrated the ability to reverse frailty metrics—such as grip strength and gait speed—to levels comparable to younger cohorts. This is partially attributed to its interaction with Casein Kinase 2 alpha (CK2α), which promotes myogenesis and muscle repair while downregulating myostatin, a negative regulator of muscle growth.
3. Nuclear Retrograde Signaling and Cytoprotection MOTS-c is utilized to study how mitochondria signal their status to the nucleus during metabolic stress. Research indicates that upon nuclear entry, the peptide binds to Antioxidant Response Elements (ARE), driving the expression of genes involved in antioxidant defense and stress resistance. This mechanism helps protect cellular integrity against oxidative damage and nutrient deprivation.
MOTS-C: The Mitochondrial “Exercise Mimetic”
Storage & Handling Guidelines
-
Lyophilized (Powder): Stable at room temperature for shipping (up to 3 weeks). Store at -20°C for long-term stability (12–24 months). Keep desiccated and protected from light.
-
Reconstituted (Liquid): Store at 4°C (39°F).
-
Stability: Use within 2–7 days of mixing, as the peptide is unstable in solution. Do not shake during reconstitution; gentle swirling is required to preserve the alpha-helical structure.
Storage Instructions
Our products are made using a freeze-drying (lyophilization) process, which helps keep them stable during shipping for up to 3–4 months.
When the peptide is in its dry powder form, it can be stored at room temperature until you are ready to use it.
Once the peptide is mixed with bacteriostatic water (reconstituted), it should be stored in the refrigerator to maintain freshness and effectiveness. After mixing, the peptide will remain stable for up to 30 days when kept refrigerated.
Freeze-drying works by removing moisture while the peptide is frozen, leaving behind a dry, white powder that stays stable until it is rehydrated. This process helps protect the peptide and extend its shelf life.
After receiving your order, keep peptides away from direct light and heat. If you plan to use them within a few weeks or months, refrigeration below 4°C (39°F) is recommended, though short-term room-temperature storage is generally acceptable for dry peptides.
For long-term storage (several months to years), peptides should be kept in a freezer at −80°C (−112°F) to best preserve their quality and stability.



